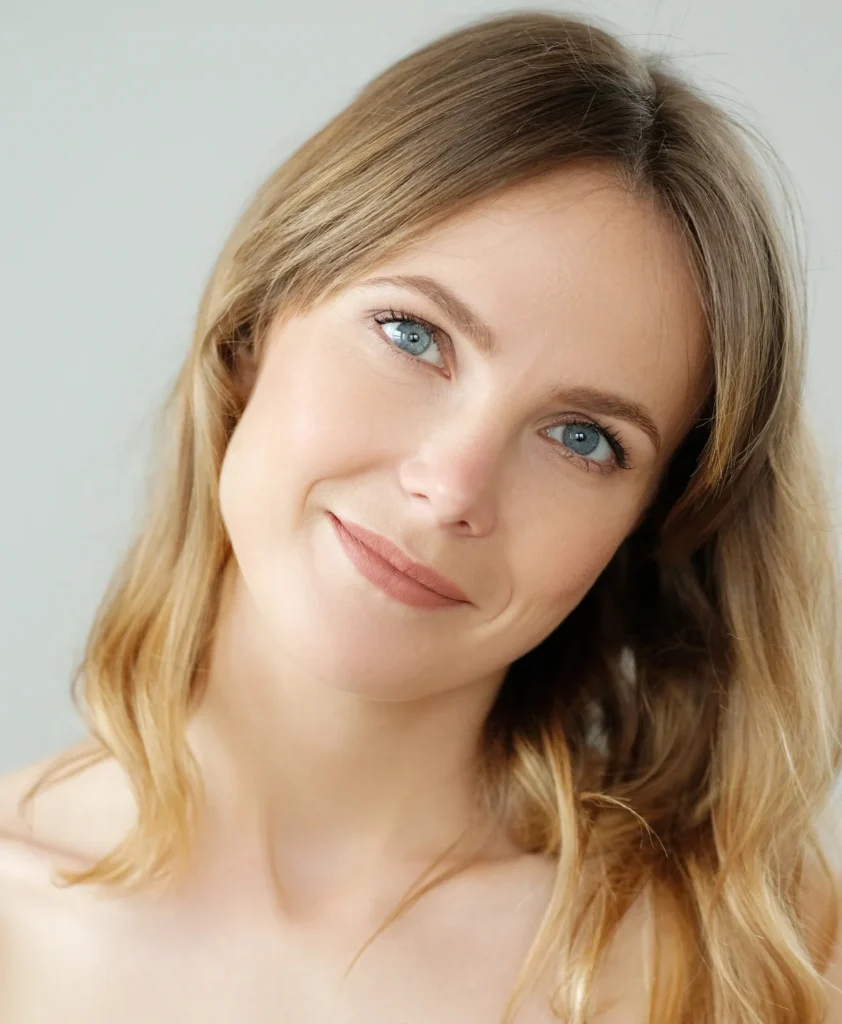
Gentle care. Advanced treatment. Visible results. Hemangiomas are benign vascular growths—often appearing as red or purple “birthmarks”—that typically develop in infants but can also appear later in life. While many hemangiomas shrink on their own, others grow rapidly or leave behind cosmetic or structural concerns that require expert intervention. At our clinic, we offer safe, effective, and minimally invasive treatment options to reduce or remove hemangiomas—improving both appearance and comfort while minimizing scarring or tissue damage. Every case is handled with care, precision, and a deep understanding of both medical and aesthetic outcomes.
Schedule Your Appointment
Secure Your Appointment in Just a Few Clicks.
Schedule Your Appointment
Secure Your Appointment in Just a Few Clicks.
- Home
- About Us
- Procedures
- Testimonials
- Before/After
- Liposuction Before/After Results
- Tummy Tuck Before/After Results
- Gynecomsatia Before/After Results
- Breast Augmentation Before/After Results
- Facelift Before/After Results
- Brazilian Butt Lift Before/After Results
- Fat Transfer Before/After Results
- Double Chin Before/After Results
- Hair Transplant Before/After Results
- Nose Surgery Before/After Results
- Hemangioma Before/After Results
- Ear Correction Before/After Results
- Videos
- Blog
- Contact Us
- +92 300 101 4047
- Our Locations
Schedule Your Appointment
Secure Your Appointment in Just a Few Clicks.